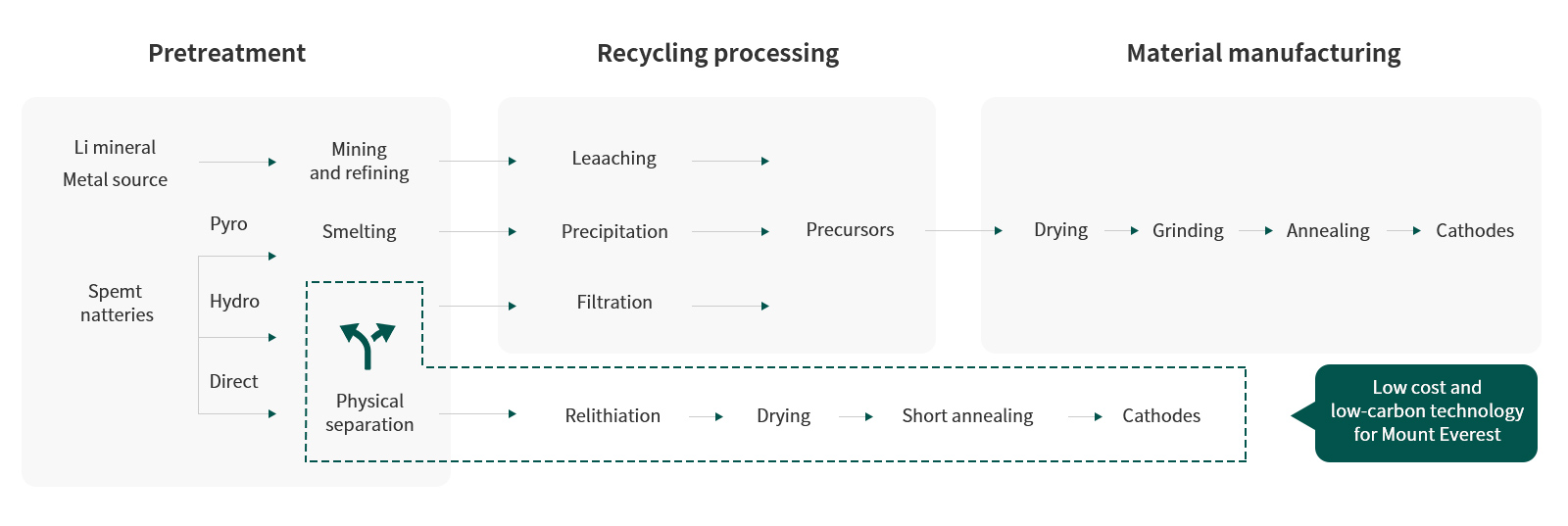
Recycling Process
—
The current conventional recycling method uses traditional non-ferrous smelting methods to achieve element level recovery by destroying the crystal structure, which has disadvantages such as low utilization rate, high energy consumption, and secondary pollution.
Process comparison
—

Fixed investment

Environmental protection

Energy consumption

Rate of recovery
Traditional recycling method
Chemical land is required, with high land and construction costs
High investment in production line equipment
Using acid and alkali to produce waste liquid and exhaust gas
Complex process and high energy consumption
Old materials ->precursors ->new materials
Low recycling rate, generating a large amount of solid waste
Ruikemei fully dry process
No need for chemical land, factory buildings can be leased
Low investment in production line equipment
No need for acid or alkali, no waste liquid or gas
Short process, new benchmark for carbon reduction
Old materials ->New materials
Comprehensive energy consumption<1200kWh/t
Comprehensive recovery rate>99%, no solid waste
Traditional recycling method
Chemical land is required, with high land and construction costs
High investment in production line equipment
Using acid and alkali to produce waste liquid and exhaust gas
Complex process and high energy consumption
Old materials ->precursors ->new materials
Low recycling rate, generating a large amount of solid waste
Core equipment
—
1 Fully automatic disassembly
Beat<10s, processing capacity of 1.8 tons/h
2 Accurate separation
Positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, and separator discharge independently
3 Strong compatibility
Capable of handling various sizes and multi roll core batteries
4 Strong security
Operating under negative pressure environment to prevent electrolyte leakage
5 Reduce costs and emissions
Adopting electrolyte condensation recovery technology (>95%) to minimize exhaust emissions and reduce exhaust treatment costs to the greatest extent possible

Case Presentation
—




